The 12-lead ECG is a fundamental diagnostic tool for assessing cardiac electrical activity. Accurate electrode placement ensures precise recordings, enabling effective diagnosis of heart conditions and monitoring.
1.1 Overview of 12-Lead ECG
A 12-lead ECG is a comprehensive tool for assessing the heart’s electrical activity, providing a detailed view of cardiac function from multiple angles. It uses 10 electrodes placed on the body to generate 12 leads, offering insights into various cardiac conditions. This diagnostic method is widely used in both clinical and non-clinical settings to detect abnormalities such as ischemia, arrhythmias, and structural heart diseases. The 12-lead system is standardized, ensuring consistency in recordings and interpretations across different devices and settings. Its versatility allows it to be used in emergency situations, routine check-ups, and long-term monitoring, making it a cornerstone of cardiovascular care and diagnosis.
1.2 Importance of Accurate Electrode Placement
Accurate electrode placement is crucial for obtaining reliable 12-lead ECG readings. Misplacement can lead to inaccurate or misleading results, potentially causing incorrect diagnoses or delayed treatment. Proper positioning ensures that each lead captures the correct electrical signals from the heart, providing a clear and precise representation of cardiac activity. Consistent placement also allows for comparability between serial ECGs, aiding in the detection of subtle changes over time. Furthermore, accurate placement minimizes artifacts and interference, enhancing the quality of the recording. Adhering to standardized guidelines ensures that healthcare professionals can confidently interpret ECGs, making it a critical step in patient care and management.
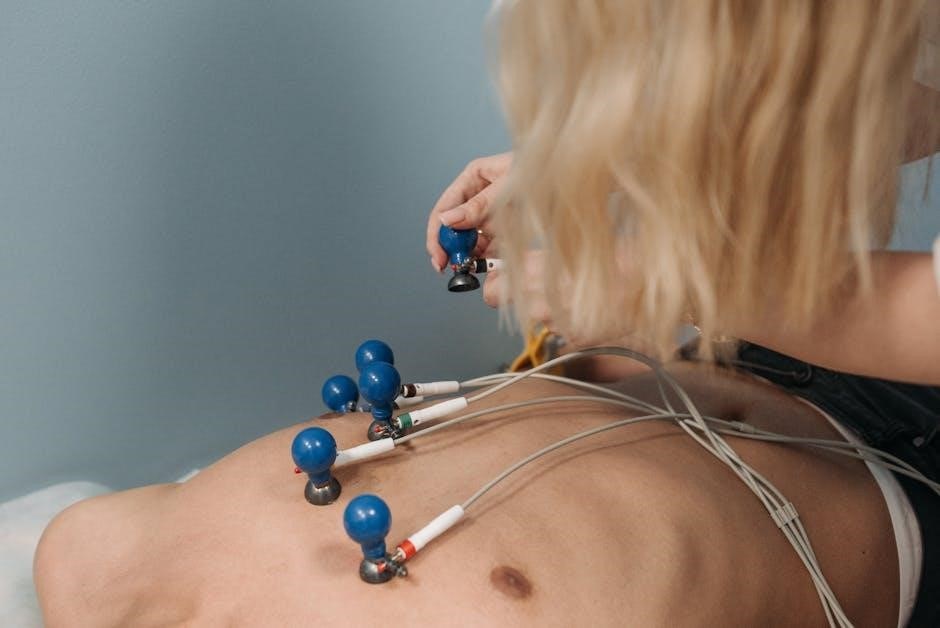
Fundamentals of 12-Lead ECG Electrode Placement
The fundamentals of 12-lead ECG electrode placement involve standard locations for limb and chest leads. Consistent placement is key for accurate readings, avoiding bone and ensuring proper alignment, especially in female patients.
2.1 Standard Placement Locations for Limb Leads
The standard placement for limb leads involves positioning electrodes on the arms and legs. The RA (right arm) and LA (left arm) electrodes are placed on the distal ends of the wrists, while the RL (right leg) and LL (left leg) electrodes are positioned on the medial aspects of the ankles. It is crucial to avoid placing electrodes directly over bones or joints to minimize interference. For consistency, electrodes should be placed 1-2 cm away from the wrists and ankles. Proper placement ensures accurate recordings and avoids artifacts. Consistency across placements is vital for reliable ECG interpretations. Always refer to standardized guidelines for precise locations.
2.2 Proper Placement of Chest Leads
Proper placement of chest leads (V1-V6) is critical for capturing accurate anterior and lateral heart activity. V1 and V2 are placed at the fourth intercostal space, right and left of the sternum, respectively. V3 is midway between V2 and V4. V4 is at the fifth intercostal space, mid-clavicular line. V5 and V6 are placed horizontally aligned with V4, in the anterior axillary line. For female patients, chest leads should be placed under the breast tissue to avoid interference. Consistent placement ensures comparability of ECGs over time. Always use anatomical landmarks to guide placement and ensure electrodes are firmly attached to the skin for clear signals. Correct positioning minimizes artifacts and enhances diagnostic accuracy.
2.3 Key Anatomical Landmarks for Electrode Placement
Accurate electrode placement relies on identifying key anatomical landmarks. The manubrium of the sternum is the reference point for limb leads (RA, LA, RL, LL). Chest leads (V1-V6) are placed based on intercostal spaces and rib alignment. V1 and V2 are at the 4th intercostal space, right and left of the sternum. V4 is at the 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line. V3 is midway between V2 and V4, while V5 and V6 are placed anterior to the mid-axillary line. Proper alignment ensures electrodes avoid bony structures and breast tissue, optimizing signal clarity. Palpation of landmarks is essential for precise placement, ensuring reliable ECG recordings.
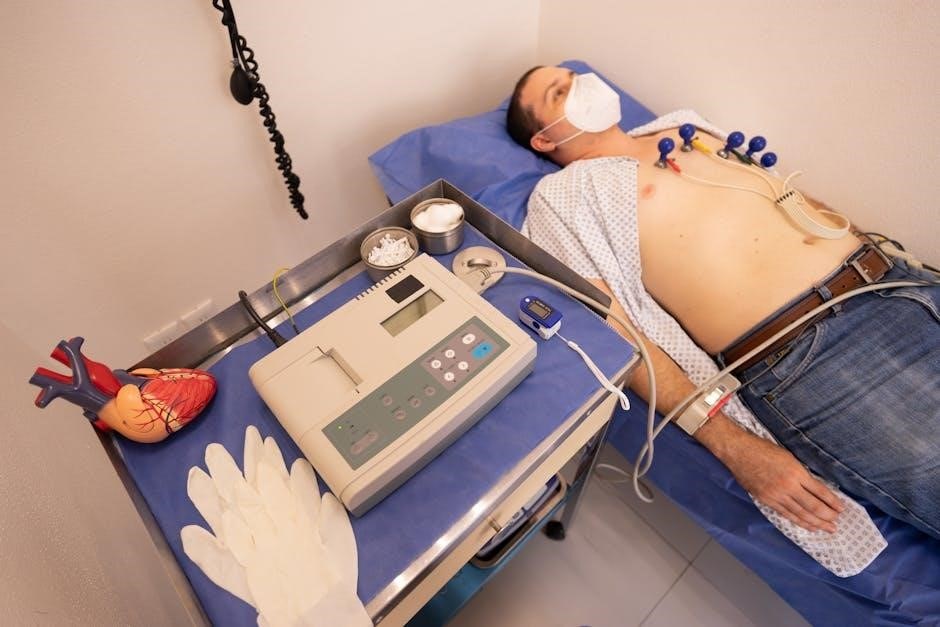
Step-by-Step Guide to 12-Lead ECG Placement
This guide provides a structured approach to placing electrodes for a 12-lead ECG, ensuring accuracy and patient comfort. Follow the sequence for optimal results.
3.1 Preparing the Patient and Equipment
Begin by explaining the procedure to the patient and ensuring they are comfortable. Position the patient in a supine position with arms at their sides. Remove jewelry and clothing that may interfere with electrode placement. Clean and dry the skin to ensure good electrode adhesion, using alcohol pads if necessary. Gather all necessary equipment, including electrodes, leads, and the ECG machine. Turn on the device and perform a quick calibration check. Ensure the environment is quiet and free from interference to minimize artifact. Proper preparation ensures accurate readings and a smooth process for both the patient and technician.
3.2 Placing Limb Electrodes (RA, LA, RL, LL)
Place the RA electrode on the right arm, 1-2 cm above the wrist, on the lateral (outer) aspect. The LA electrode goes on the left arm, mirroring the RA; For the lower limbs, position the RL electrode on the right leg, 1-2 cm above the ankle on the lateral aspect, and the LL electrode on the left leg, similarly placed. Ensure electrodes are not placed over joints or bony prominences. Secure them firmly to prevent movement and ensure good adhesion. This placement minimizes interference from muscle activity and ensures accurate recordings of the heart’s electrical activity;
3.3 Placing Chest Electrodes (V1-V6)
Begin by locating the fourth intercostal space at the midclavicular line for V1 and V2. Place V1 to the right of the sternum and V2 to the left. V3 is positioned midway between V2 and V4. V4 goes at the midclavicular line in the fifth intercostal space. V5 is placed in the anterior axillary line at the same level as V4, and V6 is further along the midaxillary line. Ensure electrodes are aligned horizontally and secured firmly, avoiding hair or muscle tissue for clear signals. Proper placement ensures accurate capture of the heart’s electrical activity from the chest leads.
Tips for Optimal ECG Readings
Ensure proper skin preparation, minimize interference, and secure electrodes firmly to avoid artifacts. Maintain a calm, still patient and use high-quality equipment for clear, accurate recordings.
4.1 Ensuring Proper Skin Preparation
Proper skin preparation is essential for obtaining high-quality ECG readings. Clean the skin thoroughly with alcohol to remove oils, lotions, or dirt, ensuring good electrode adhesion. Shave hairy areas if necessary to prevent interference. Avoid using excessive force, which may irritate the skin. Dry the area completely before placing electrodes, as moisture can cause artifacts. Ensure the skin is free from oils or residues, as this can impede electrode conductivity. Proper preparation minimizes noise and ensures accurate electrical signals are captured, leading to reliable ECG results. This step is critical for both initial and follow-up recordings to maintain consistency and comparability.
4.2 Minimizing Artifact Interference
Artifact interference can significantly distort ECG readings, leading to inaccurate interpretations. Common sources include muscle movement, electrical interference, and poor electrode adhesion. To minimize artifacts, ensure electrodes are securely placed on clean, dry skin and avoid areas with excessive hair or scar tissue. Use high-quality electrodes and maintain a quiet, stable environment during the recording. Patient movement should be discouraged, and electrical devices nearby should be turned off. Consistent electrode placement and proper skin preparation are also critical. Regularly inspect electrodes for loose connections, and ensure the ECG machine is calibrated correctly. By addressing these factors, you can reduce interference and obtain clearer, more reliable ECG tracings.
Troubleshooting Common Placement Errors
Identify misplaced electrodes by checking lead positioning and skin preparation. Correcting errors involves repositioning electrodes and ensuring proper adhesion to avoid signal distortions and inaccurate readings.
5.1 Identifying and Correcting Misplaced Electrodes
Accurate electrode placement is critical for clear ECG readings. Misplaced electrodes can lead to artifacts or inaccurate tracings. Common errors include incorrect limb lead placement, improper chest lead positioning, or failure to align electrodes with anatomical landmarks. To identify issues, inspect electrode positions and compare the ECG tracing to baseline norms. Correct misplaced electrodes by repositioning them according to standard guidelines, ensuring proper adhesion and skin contact. Pay special attention to chest leads, as small deviations can significantly affect readings. Verifying electrode placement before recording ensures reliable results and accurate cardiac assessments. Always refer to standardized protocols to maintain consistency and diagnostic accuracy;
5.2 Avoiding Errors in Chest Lead Placement
Accurate chest lead placement is vital for obtaining clear ECG readings. Errors often occur due to incorrect positioning or failure to align leads with anatomical landmarks. To avoid mistakes, ensure V1 and V2 are placed at the 4th intercostal space, near the sternum. V3 should be midway between V2 and V4, while V4 is at the 5th intercostal space, midclavicular line. V5 and V6 are placed horizontally aligned with V4, at the anterior axillary line. Use a stethoscope to locate the apical beat for precise V5 and V6 placement. Avoid placing leads over muscle or bone, as this can cause interference. Properly secure electrodes to prevent movement artifacts and ensure consistent, high-quality recordings. Regularly verify lead positions to maintain diagnostic accuracy and reliability.

Special Considerations
Accurate 12-lead ECG placement varies for female, pediatric, and geriatric patients. Adjustments ensure proper electrode positioning, avoiding interference from breast tissue in women and accommodating smaller body sizes in children and elders.
6.1 Electrode Placement in Female Patients
Proper 12-lead ECG electrode placement in female patients requires careful consideration to avoid interference from breast tissue. Chest leads (V1-V6) should be placed under the breast tissue when necessary, ensuring direct contact with the skin. Avoid placing electrodes on dense breast tissue to minimize artifacts. For limb leads, standard placements apply, but ensure electrodes are secure and comfortable. Skin preparation is crucial to enhance conductivity and reduce motion artifacts. Additionally, electrode adhesion should be checked to prevent displacement during movement. Accurate placement ensures reliable ECG readings, aiding in precise cardiac assessments for female patients.

6.2 Placement in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients
In pediatric patients, accurate 12-lead ECG placement requires adjusting for smaller body sizes. Limb electrodes should be proportionally placed, and chest leads (V1-V6) positioned according to the child’s anatomy. Geriatric patients may need electrodes placed carefully due to skin fragility or folds. Ensure electrodes adhere securely without causing discomfort. For both groups, skin preparation is vital to enhance conductivity. In pediatric cases, minimize movement to avoid artifacts. Geriatric patients may require additional time for electrode placement due to potential subcutaneous fat or bony prominences. Tailoring techniques to these populations ensures high-quality ECG recordings and accurate cardiac assessments.
Accurate 12-lead ECG placement is vital for reliable cardiac assessments. Proper electrode positioning and adherence to best practices ensure optimal recordings, aiding in precise diagnoses and effective patient care.
7.1 Summary of Best Practices
Accurate 12-lead ECG placement requires meticulous attention to detail. Ensure proper skin preparation by cleaning and drying the skin to enhance electrode adhesion and signal quality. Always use standardized electrode positions, avoiding bone and placing chest leads consistently. Minimize artifacts by ensuring the patient remains still, avoids talking, and keeps muscles relaxed during the recording. Verify electrode placement and connection before starting the ECG to prevent errors. Use high-quality electrodes and ensure proper equipment calibration. Consistency in lead placement across recordings is crucial for accurate comparisons. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for equipment use and maintenance. Proper documentation and verification of electrode placement are essential for reliable results.
7.2 Resources for Further Learning
For deeper understanding, explore comprehensive guides like the American Heart Association’s ECG Handbook or online courses from platforms like Coursera and Udemy. Websites such as ECGLibrary and Medical Training Institute offer detailed tutorials and diagrams. The British Journal of Cardiology publishes evidence-based articles on ECG interpretation. Additionally, video tutorials on YouTube channels like MedCram provide visual aids for electrode placement. Interactive tools, such as ECG simulators, allow hands-on practice. Always refer to peer-reviewed journals and reputable medical websites for updated practices. These resources help healthcare professionals refine their skills and stay current with advancements in 12-lead ECG placement and interpretation.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.